What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a tool that enables website owners to manage and deploy marketing tags on their website without needing to modify the code.
These tags include Google Analytics, Google Ads, and other tracking codes that provide insights into a website’s performance. These insights help website owners update and optimize their website and its content based on real-life user interactions and performance statistics.
Common uses of Google Tag Manager include:
- tracking website page view
- tracking button clicks
- tracking external links/outbound clicks
- tracking conversions, such as in Google Ads
- tracking how a user scrolls and behaves on a page
- collecting user data, such as geolocation, device type and even screen width.
If this gets too technical, then think of it this way:
If your website is a symphony hall and the tags are all the different musicians you’ve chosen to house, then Google Tag Manager is the conductor. The conductor chooses what instruments are to play and when they are to play, in what order and for what duration.
How does Google Tag Manager work?
Google Tag Manager works through tags and triggers.
Tags are pieces of code, such as HTML or JavaScript, which are deployed on your website for analytics or marketing purposes, or it could be a social media plugin as well. They are also known by names such as tracking pixel, web beacons, ultrasound beacons and many others depending on their functions.
Collections of tags, such as “marketing”, are called tag containers.
Triggers are the conditions under which tags are allowed to fire. Google Tag Manager can control when a certain tag is fired.
Imagine a user is browsing a clothing website and clicks on a product. You can set a trigger in Google Tag Manager to fire a tag when this specific click event occurs. This tag might then send information to an analytics tool like Google Analytics, recording that the user showed interest in that particular product. This action-trigger relationship helps the website owner understand user behavior and preferences based on specific interactions on the website.
These rules can be URL-based or event-based, such as when a user scrolls or clicks on some area of your website.
In other words:
- tags are what happens
- triggers are when they happen
Most third-party tags (tags from other websites, not the one the user is browsing) will set third-party cookies that, according to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require the explicit prior consent of your users.
Why is cookie consent important?
The concept of cookie consent gives website visitors the power to choose whether they agree to let companies collect their data. It is a legal requirement under privacy laws like the GDPR. The significance of cookie consent is highlighted by the fact that many people prefer not to do business with companies that share their sensitive data without permission. With cookies being a common method for data collection, obtaining cookie consent has become a crucial aspect of managing an online business.
Does Google Tag Manager use cookies?
Google Tag Manager does not set cookies on its own, with one exception — when someone uses its preview and debug mode. During this specific scenario, Google Tag Manager sets first-party cookies, enabling users to observe which tags are being activated on each page.
These cookies affect only the user who has activated the preview and debug mode and do not impact regular website visitors. Importantly, once the user exits the preview mode, these cookies are deleted.
Does Google Tag Manager require cookie consent?
Google Tag Manager doesn’t directly require cookie consent because it doesn’t set cookies — it’s a tool used for adding and managing tracking tags on a website.
However, some of the tags added through Google Tag Manager may use cookies to track how users interact with a website, which makes obtaining cookie consent necessary to meet GDPR guidelines. Combining Google Tag Manager with a Consent Management Platform (CMP) enables website owners to correctly manage user consent for cookies.
Is Google Tag Manager GDPR compliant?
The GDPR, which came into force in May 2018, has strict rules about what you can do on your website with cookies.
The European Union (EU) law is binding in all 27 member states, and if you have visitors from the EU, you are obligated to abide by the rules, even if you and your website are located outside the EU.
So, if you have any type of cookie or tracking technology on your website, the GDPR states that you must:
- Obtain clear and unambiguous consent from its users,
- Prior to any processing of personal data,
- After specifying all types of cookies and other tracking technology present and operating on its pages,
- In easy-to-understand ways that enable users to consent and to revoke consent on each specific category of cookies,
- To then be able to safely and confidently document each user consent,
- Consent must be renewed annually. However, some national data protection guidelines recommend more frequent renewal, e.g. 6 months. Check your local data protection guidelines for compliance.
Google Tag Manager is a tool designed to manage and deploy tags on a website and doesn’t inherently violate the GDPR. However, its compliance with the GDPR depends on how it is used.
The compliance aspect comes into play when considering the type of data these tags collect and how. Website owners are responsible for ensuring that the tags deployed through Google Tag Manager comply with the GDPR, which includes obtaining legally valid consent from users for data collection and processing activities.
Respecting consent status with Google Consent Mode in Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager can be used with Google Consent Mode to ensure that tags don’t fire unless a user has explicitly consented to having their data collected. Google Consent Mode, an open API developed by Google, enables websites to control if and when tags should fire, which depends on users’ consent choices.
Google Consent Mode can be used for various Google services, including Google Analytics, Google Tag Manager, and Google Ads. It can also be used to signal consent state for third-party tags (for non-Google products and services) with additional configurations.
The Consent Initialization trigger plays a significant role in Google Consent Mode. It ensures that all consent settings are implemented before any other triggers prompt tags to fire.
Using Google Consent Mode and Google Tag Manager together can help website owners respect users’ consent preferences and privacy and stay compliant with data protection regulations like the GDPR that mandate prior consent to obtain data.
How Cookiebot™️ can help you comply with cookie laws when using Google Tag Manager
Cookiebot CMP is a cookie consent solution and consent management platform for your website that enables you to make sure that your domains’ use of cookies and tracking is GDPR compliant.
1. Scans your website for cookies
The Cookiebot CMP technology first scans your website and all of its subpages, finding all cookies and similar tracking technologies present – without exception (everything from HTTP/JavaScript cookies, HTML5 Local Storage, Flash Local Shared Object, Silverlight Isolated Storage, IndexedDB, ultrasound beacons, pixel tags… and the list goes on).
Scan your website for free to learn what cookies it uses.
2. Creates a cookies policy
Cookiebot CMP then generates a cookie declaration with descriptions of every cookie found on your website that can be used as part of your consent dialog’s details and as a separate cookie report, integrated in your privacy policy.
3. Enables customizable consent banners
After Cookiebot CMP completes its scan, our customizable consent banner will display all the cookies and trackers on your website within four categories, three of which (preferences, statistics and marketing) the user can give and revoke their consent to.
4. Obtains and records legally valid user consent
The user then gives their consent and based on the specifics of this consent (e.g. whether they opted in for marketing cookies, or out of analytics), the cookies and trackers are then activated on your website.
5. Allows tags to fire based on user consent
Cookiebot CMP automatically controls all cookies so that no user data is collected until your users give consent, as mandated by the GDPR. Cookiebot CMP then tells Google Tag Manager what tags to run.
Only strictly necessary cookies are allowed to be set when a user arrives on a website, and consent banners that manage user consent are not allowed to have pre-ticked checkboxes on any other categories of cookies.
If the user decides to not have marketing or analytics cookies set on their devices, Cookiebot CMP changes the conditions for which Google Tag Manager runs tags, and so will not run tags that set marketing or analytics cookies.
Cookiebot CMP acts like the privacy protecting bridge intermediary that controls what Google Tag Manager is allowed to do based on the specifics of your users’ consent.
By using Cookiebot CMP, you can ensure that the cookies and trackers that you deploy as tags through Google Tag Manager meets GDPR cookie consent requirements, i.e. doesn’t collect personal information on users before they’ve given their consent to it.
6. How do Cookiebot CMP and Google Consent Mode work together?
Cookiebot CMP integrates Google Tag Manager with Google Consent Mode using a Tag Manager template designed to work with the Consent API and easy to set up without heavy coding knowledge.
Cookiebot CMP manages the consents of your users and communicates their consent state to the Google Consent Mode API that governs the behavior of all Google-services based on user consents.
If a user doesn’t give consent to statistics or marketing cookies, Google Consent Mode makes sure that you still get valuable insight into your website’s performance while respecting end-user privacy.
Google Consent Mode ensures aggregate and non-identifying data if users don’t consent to cookies, including:
- timestamps
- user agents
- referrers
- other basic measurements for modeling
Google Consent Mode also enables you to display contextual ads based on anonymous data instead of targeted ads based on personal data, if users don’t give their consent to marketing cookies.
How to implement Google Tag Manager with Cookiebot CMP
In order to “get the best of both worlds” – meaning website optimization through analytics and marketing, as well as being GDPR compliant and respecting your users’ privacy – you need to make sure that:
- The Google Tag Manager script is the first script to load on your website.
- Your Google Tag Manager script is marked with: data-cookieconsent=”ignore” to ensure that Google Tag Manager will always be allowed to load.
- You insert the Cookiebot script with automatic cookie blocking immediately after the Google Tag Manager script.
- Create 3 triggers in Google Tag Manager, which are fired upon custom event cookie_consent_[category] category = {preferences, statistics, marketing}
Here is an example of how that looks –
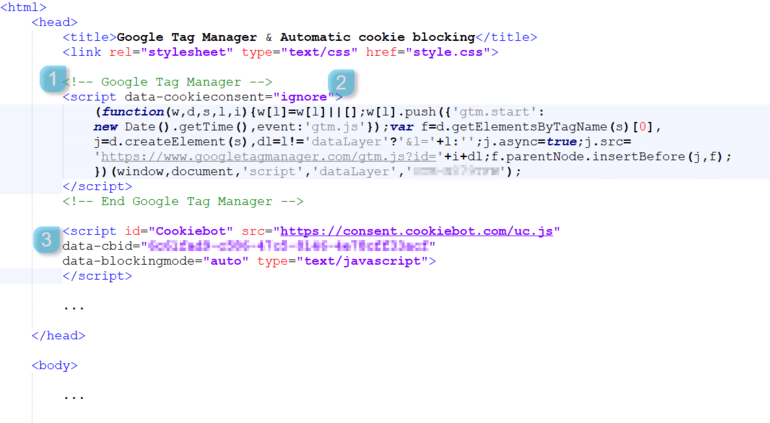
To know more about the technical aspects of the implementation, check out our support page dedicated to Google Tag Manager and Cookiebot CMP.
Implications of the Digital Markets Act (DMA) on Google Tag Manager
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) places strict emphasis on obtaining clear and affirmative user consent for data collection in line with the GDPR. All tags deployed through Google Tag Manager must comply with these consent standards, and businesses that use Google Tag Manager will need to adapt to the DMA’s requirements in how they manage tags that collect user data.
This adaptation may involve modifications in tag setup and trigger mechanisms based on user consent. The approach to tag management will need to become more dynamic, with user consent directly influencing which tags are active at any given time, ensuring that they follow the DMA’s requirements.
The DMA law applies to gatekeepers (including Alphabet, which owns Google and its products), who are liable for DMA compliance. However, businesses that don’t collect consent as per the DMA’s requirements — which align with the consent requirements under the GDPR — risk losing access to gatekeepers’ products and services and face hefty penalties under the GDPR.
Get started on compliant Google Tag Manager cookie consent today with Cookiebot CMP
Start your 14-day free trial of all premium features
FAQ
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a popular tool for controlling tags on websites. Google Tag Manager can be used to control everything from statistical scripts or marketing tags that collect data for analytics and advertising, like tracking website page views, button clicks and how users scroll and behave. Websites use Google Tag Manager to update and optimize their websites and its content based on tracking of user interactions.
Google Tag Manager works through tags and triggers. Tags are pieces of code that are embedded on a website by Google Tag Manager that set trackers such as tracking pixels, web beacons or ultrasound beacons, depending on their technology. Triggers are the conditions under which tags are activated, e.g. when a user clicks or scrolls. Almost all third-party tags will set cookies on users’ browsers and therefore require the consent of users before activation.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU data privacy law that, along with the ePrivacy Directive (also known as the “cookie law”), governs the processing of personal data of individuals inside the EU. The GDPR requires websites to obtain the clear and affirmative consent from users before being allowed to activate cookies that process personal data, such as IP addresses, browser and search history.
Google Tag Manager can be used to deploy analytics and marketing cookies on your website, which means that you will need the prior consent from users in order to lawfully use Google Tag Manager in the EU. Statistics and marketing cookies must be deactivated by default until a user has given their prior consent.
Google Tag Manager does not set cookies on its own except when someone uses its preview and debug mode. At this time, it sets first-party cookies for the user to observe which tags are being activated on each page. Only the user who has activated the preview and debug mode is impacted, and these cookies are deleted once they exit preview and debug mode.
Google Tag Manager doesn’t collect personal information itself, but it does enable third-party tags to do so. The GDPR requires any organization that collects personal data from EU residents to have transparent and comprehensive privacy and cookies policies in place that share information about what data is collected, for what purpose, how long it’s stored for, and who has access to it.
If you use Google Tag Manager to control the tags on your website, you must have a privacy policy in place with a section on cookies (or a separate cookies policy) to communicate your data collection policies to users.
Google Tag Manager helps SEO professionals gain more insights into the activities on a website by managing the tags that collect information on user actions such as scrolling, link clicks, form submissions, video views, and more. The gathered data can then be analyzed using Google Analytics, helping to understand user behavior and improve website engagement. Google Tag Manager keeps your tags and code snippets organized, which contributes to a better user experience and efficient running of your site — factors which are important for SEO.
Google Tag Manager (GTM) does not set cookies itself, but can read cookies set on a user’s browser, using either its built-in variables or custom JavaScript variables. This feature enables Google Tag Manager to access and use cookie values for various applications, such as personalizing website content based on user preferences, enhancing tracking and analytics by observing user behavior, and supporting targeted advertising strategies through remarketing efforts. The use of cookie data in Google Tag Manager enables more tailored and effective management of website interactions and marketing initiatives.
Google Tag Manager may be affected by ad blockers, particularly if it’s used to deploy advertising or tracking tags. The extent to which Google Tag Manager is blocked depends on the type of tags used, the specific criteria of the ad blocker, individual user settings, and ongoing updates to ad blocker algorithms. While Google Tag Manager is not inherently an advertising tool, its association with Google’s advertising services can lead to its tags being blocked, potentially impacting website analytics and functionality. Even though this differs from ad blocker to ad blocker, website managers should consider this in their traffic analysis and site maintenance strategies.
Resources
See our guide for deploying Cookiebot CMP in Google Tag Manager
Cookiebot CMP tag in GTM Community Template Gallery
Get started with Google Consent Mode
Learn more about the GDPR and what it requires of your website